FAIR Data Principles
What is FAIR Data?
The FAIR Data Principles where published in 2016 by a consortium of organisations and researchers who not only wanted to enhance the reusability of datasets, but also related facets such as tools, workflows and algorithms. The principles developed addressed four key aspects of making data Findable, Accessible, Interoperable and Reusable (FAIR).
- Findable – Data and metadata should be easily discoverable by both humans and machines through the use of standard identification mechanisms.
- Accessible – Once found, data should be easy to download and use either locally or in a trusted digital research environment. The hosting repository should also have plans in place to keep metadata accessible even in the event of the data itself no longer being available.
- Interoperable – Utilise standard vocabularies and ontologies in order to ensure the data can be easily mapped and combined with other datasets. This, along with the ability to transform data into standardised formats like FHIR, enables sharing between various scientific disciplines and organisations.
- Reusable – Data and metadata should be richly described with the least restrictive licenses, allowing it to be easily reused in future research. Integration with other data sources should be easy, facilitated by proper citations and descriptions. The standard identification of items improves data provenance and allows researchers to not only re-use data, but to identify how aspects of it may be reproduced in their own research.
FAIR Data Services Overview
ADDI FAIR Data Services gives researchers and innovators the ability to discover and understand data through dataset search, classification and efficient metadata browsing capabilities described via dataset catalogues, dictionaries and associated attached assets. Researchers can request access to datasets where data owners can review and either approve or deny where approval unlocks an action such as data delivery to an ADDI Workspace.
Key Features
| Feature | Key Points |
|---|---|
| Data Discovery |
|
| Request Access to Data |
|
| Metadata Browsing |
|
| Metadata Management |
|
| Role-based Access Control |
|
| Built on Standard |
|
| Integration with Aridhia Workspace |
|
| Privacy by Design |
|
| Cloud-native Service |
|
FAIR Permission Model
The permission model of FAIR Data Services is made up of three levels:
- Admin-level permission: privileges to administer the service.
- Dataset-level permission: privileges related to datasets and features where the dataset is the core entity (e.g. search)
- Dataset-level visibility: the level of visibility a dataset has within the service to other users.
A high-level summary of the permission model is shown below:
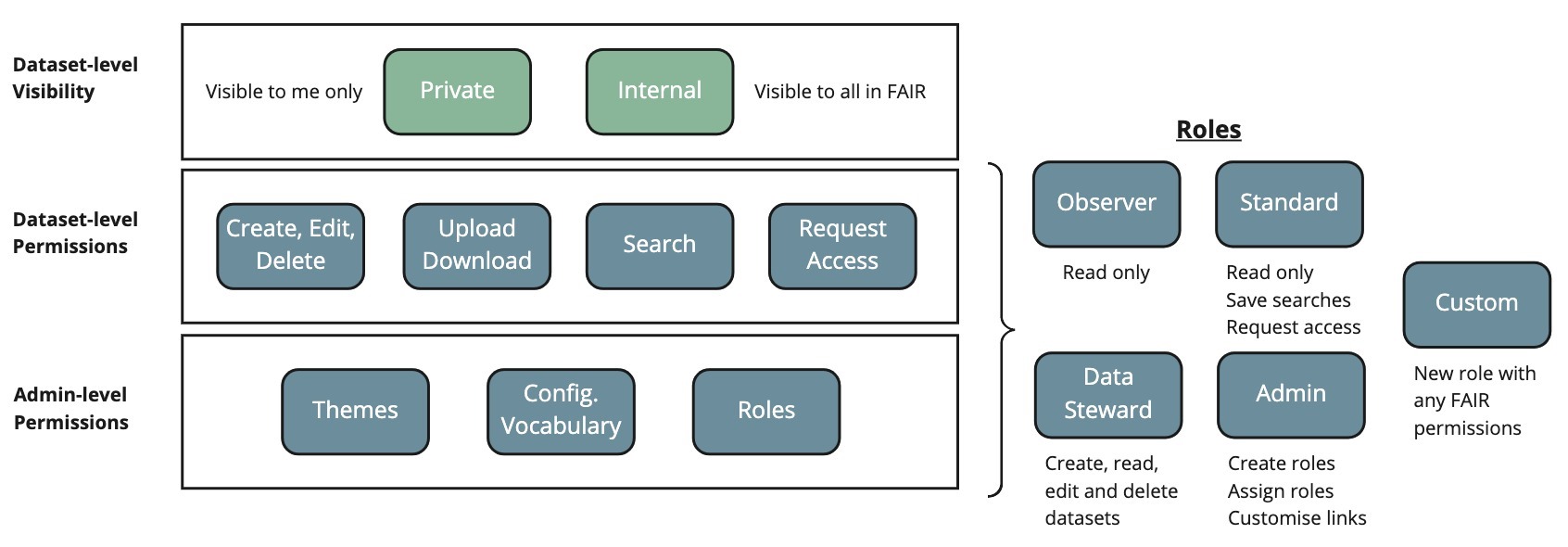
Roles
Roles are groupings of permissions. Four managed roles exist that group together permissions from either administration or dataset-level permissions. Custom roles can be created that can mix and match between administration and dataset-level permissions. See the ‘Role-based Access Control’ article for more information about available roles, creation and assignment to users.
Admin-level Permissions
Administration permissions are those that allow you to administer the service. This includes:
- Creating roles and assigning roles to users.
- Configuring the service to use custom links via the Configuration Vocabulary.
- Setting a predefined theme for the user interface to adopt.
These permissions are currently available to users that have the Admin role however a custom role can be created to adopt all or some of these permissions along with others. See the ‘FAIR Permissions’ article for a list of all permissions available in FAIR.
Dataset-level Permissions
Dataset-level permissions are those related to datasets as well as features where the dataset is the core entity. Specifically these permissions allow the ability to:
- Create, read, edit and delete dataset entries
- Download metadata of a dataset entry
- Upload data (e.g. csv) to the dataset entry
- Search for datasets
- Request access to a dataset
See the ‘FAIR Permissions’ article for a list of all permissions available in FAIR.
Dataset Visibility
The visibility of a dataset to other users in the service can be defined either at the time of creation or modified after creation. The visibility of the dataset is specified within the dataset and is not an explicit permission that can be assigned to a role. More information regarding dataset visibility, see the ‘Dataset Visibility’ article.